
Coronary Artery Scan: What It Shows and Why It Matters for Prevention
Coronary Artery Scan: What It Shows, Who Needs It, and
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy production, and hormonal balance. When the thyroid is not functioning properly, it can lead to numerous health issues that can affect overall well-being. Thyroid problems are remarkably common, affecting millions of people worldwide, but they are often underdiagnosed. Understanding and identifying thyroid issues early on can prevent complications and support a better quality of life.
Life Imaging Fla, a leading imaging center specializing in early detection of heart disease and cancer, also focuses on identifying thyroid problems through advanced screening tests. Utilizing state-of-the-art imaging technology, Life Imaging Fla provides a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and monitoring thyroid conditions, ensuring prompt and accurate results.
Different types of thyroid issues, such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer, can present with varying symptoms that complicate diagnosis without proper screening. Common symptoms often overlap with other health conditions, making thorough screening essential. This article delves into the most prevalent thyroid issues, elaborates on the importance of early detection, and explains the various screening tests available to maintain optimal thyroid health.
By understanding these aspects and recognizing the significance of early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their thyroid health effectively. At Life Imaging Fla, the use of advanced imaging techniques offers patients reliable insights into their thyroid health, enabling timely and appropriate medical interventions.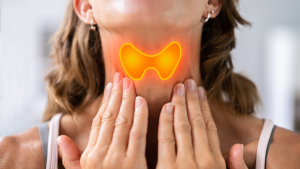
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. This condition can lead to a slowdown in various body functions.
– Common Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, dry skin, and hair loss are typical symptoms of hypothyroidism. These symptoms can gradually develop and often go unnoticed for a long time.
– Causes: The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the thyroid gland. Other causes include iodine deficiency, certain medications, and treatments for hyperthyroidism.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism are essential to avoid complications like heart disease and mental health issues.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, speeding up the body’s metabolism.
– Common Symptoms: Symptoms include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, sweating, nervousness, irritability, and trembling hands. These symptoms can be mistaken for other health conditions, making proper screening vital.
– Causes: The leading cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that stimulates the thyroid to produce excessive hormones. Other causes include thyroid nodules and excessive iodine intake.
Early detection of hyperthyroidism is crucial to prevent complications such as heart problems and bone loss.
Thyroid nodules are lumps that can form within the thyroid gland. While most nodules are benign, some can be cancerous or cause thyroid dysfunction.
– Common Symptoms: Often, thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms and are discovered during routine examinations. If symptoms occur, they can include a visible lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, and sometimes hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism.
– Causes: The exact cause of thyroid nodules is often unknown, but they can be related to iodine deficiency, thyroid inflammation, or genetic factors.
Proper evaluation of thyroid nodules is crucial to determine if they pose a health risk and to decide on the best course of action.
Crucial Screening Tests for Thyroid Problems
Blood tests are fundamental tools in diagnosing thyroid conditions and monitoring treatment.
– Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Test: This is the most common test used to evaluate thyroid function. High TSH levels indicate hypothyroidism, while low levels suggest hyperthyroidism.
– Free T4 and Free T3 Tests: These tests measure the levels of free thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) in the blood. Abnormal levels can indicate thyroid dysfunction.
– Thyroid Antibody Tests: These tests detect antibodies that attack the thyroid gland, helping diagnose autoimmune thyroid disorders like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
Regular blood tests help in the early diagnosis and effective management of thyroid conditions.
Ultrasound imaging is a non-invasive method that helps visualize the thyroid gland and identify abnormalities.
– Thyroid Nodules: Ultrasound can detect and measure thyroid nodules. This imaging test helps determine whether nodules are solid or fluid-filled, guiding further evaluation.
– Structural Changes: Ultrasound is useful in detecting structural changes in the thyroid gland, such as enlargement or inflammation.
Ultrasound examinations provide valuable information for diagnosing and managing thyroid conditions.
The radioactive iodine uptake (RAIU) test helps evaluate thyroid function by measuring the amount of iodine the thyroid gland absorbs from the bloodstream.
– Diagnosis: This test is particularly useful in diagnosing hyperthyroidism and determining its cause. By analyzing how much radioactive iodine the thyroid takes up, doctors can assess if the gland is overactive.
– Thyroid Nodules: RAIU can also help in evaluating thyroid nodules by determining if they are functioning or non-functioning.
The radioactive iodine uptake test offers essential insights into thyroid activity and helps guide treatment options.
Early detection of thyroid issues is vital in preventing complications that can arise from untreated conditions.
– Heart Health: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can significantly impact heart health, leading to issues like arrhythmias, high cholesterol, and heart disease.
– Mental Health: Thyroid disorders can affect mental health, causing symptoms like depression, anxiety, and cognitive difficulties.
By catching thyroid issues early, patients can avoid severe health complications and improve their quality of life.
Early diagnosis allows for prompt and effective treatment, improving patient outcomes.
– Medications: For hypothyroidism, synthetic thyroid hormone replacements like levothyroxine can restore normal thyroid function. Hyperthyroidism treatments may include antithyroid medications, beta-blockers, or radioactive iodine therapy.
– Surgery: In cases of thyroid cancer or large nodules causing symptoms, surgical removal of the thyroid gland may be necessary.
Timely treatment helps manage symptoms and prevent the progression of thyroid disorders.
Continual monitoring of thyroid health ensures long-term well-being and effective management of the condition.
– Regular Check-ups: Periodic blood tests and physical examinations help monitor thyroid function and adjust treatments as needed.
– Lifestyle Adjustments: Patients can make lifestyle changes, such as diet modifications and stress management, to support thyroid health.
Ongoing monitoring and management are key to maintaining optimal thyroid function and overall health.
Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy
A fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is a crucial test to evaluate thyroid nodules, especially when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
– Procedure: During an FNA biopsy, a thin needle is inserted into the thyroid nodule to extract cells for examination. The procedure is minimally invasive and usually performed under ultrasound guidance to ensure accuracy.
– Diagnosis: The extracted cells are examined under a microscope to detect cancerous cells and other abnormalities. This information helps determine if the nodule is benign or malignant.
FNA biopsy is a reliable method for assessing thyroid nodules and guiding appropriate treatment plans.
The FNA biopsy offers several benefits that make it an essential tool in thyroid health management.
– Minimally Invasive: The procedure is quick and involves minimal discomfort. It does not require major surgery and has a short recovery time.
– Accurate Diagnosis: The biopsy provides precise information about the nature of thyroid nodules, aiding in the accurate diagnosis of thyroid cancer and other conditions.
Utilizing FNA biopsy improves diagnostic accuracy and supports effective treatment planning.
Thyroid Scans
Thyroid scans use radioactive iodine to evaluate the function and structure of the thyroid gland.
– Procedure: The patient swallows a small amount of radioactive iodine, which the thyroid gland absorbs. A special camera then takes images of the thyroid, showing areas of activity.
– Diagnosis: The scan helps identify conditions like hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and goiter by revealing how much iodine different parts of the thyroid absorb.
Thyroid scans provide valuable insights into thyroid activity and help diagnose various thyroid disorders.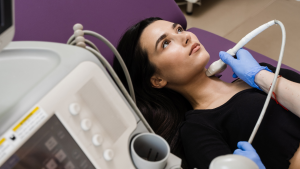
Different types of scans offer specific benefits for evaluating thyroid health.
– Thyroid Uptake Scan: This scan measures how much radioactive iodine the thyroid takes up, helping diagnose hyperthyroidism and assess thyroid function.
– Thyroid Imaging Scan: This scan produces detailed images of the thyroid, revealing structural abnormalities like nodules and enlargements.
These scans are essential tools for comprehensive thyroid evaluation and effective diagnosis.
Regular screenings play a vital role in maintaining thyroid health and catching problems early.
– Early Detection: Routine screenings can detect thyroid issues before symptoms become severe, allowing for timely intervention and better outcomes.
– Preventing Complications: Regular monitoring helps prevent complications related to untreated thyroid conditions, such as heart problems and mental health issues.
By scheduling regular thyroid screenings, individuals can stay proactive about their thyroid health.
Life circumstances and health changes can affect thyroid function, making ongoing screening essential.
– Age: Thyroid issues are more common as people age, so regular screenings become increasingly important with age.
– Pregnancy: Pregnancy can impact thyroid function, making screenings crucial for the health of both the mother and baby.
Adapting to life changes through regular screenings ensures continuous thyroid health management.
Proper diet and nutrition can significantly impact thyroid health and help manage thyroid conditions.
– Iodine Intake: Iodine is essential for thyroid function. Including iodine-rich foods like dairy products, seafood, and iodized salt can support normal thyroid activity.
– Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consuming a balanced diet with enough vitamins and minerals, such as selenium and zinc, helps maintain thyroid health.
Incorporating a healthy diet boosts thyroid function and overall well-being.
Regular physical activity supports not just general health but also thyroid health.
– Metabolism: Exercise helps regulate metabolism and supports maintaining a healthy weight, reducing stress on the thyroid.
– Stress Reduction: Physical activity can lower stress levels, which can positively impact thyroid function and reduce the symptoms of thyroid disorders.
Engaging in regular exercise promotes overall health and thyroid function.
Reducing exposure to harmful substances can protect thyroid health.
– Tobacco and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact thyroid function, increasing the risk of developing thyroid conditions.
– Environmental Toxins: Limiting exposure to harmful chemicals and pollutants helps maintain thyroid health.
By avoiding harmful substances, individuals can support their thyroid’s proper function.
Maintaining good mental health is essential for overall thyroid health.
– Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid function. Finding ways to manage stress, such as meditation and relaxation techniques, is crucial.
– Support Systems: Having a strong support system can help cope with the emotional challenges of thyroid conditions.
Prioritizing emotional well-being supports better thyroid health.
Seeking help from mental health professionals can be beneficial for managing the emotional aspects of thyroid problems.
– Therapy and Counseling: Mental health professionals can provide strategies to manage stress and emotional challenges related to thyroid issues.
– Support Groups: Joining support groups for individuals with thyroid conditions can offer emotional support and practical advice.
Professional support helps manage the stress and emotional impact of thyroid health issues.
By understanding these aspects and recognizing the significance of early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their thyroid health effectively. Incorporating regular screenings, a healthy lifestyle, and psychological support ensures comprehensive thyroid health management and overall well-being.
Understanding Thyroid Disorders in Women
Women are more likely to develop thyroid disorders compared to men.
– Hormonal Changes: Women experience more hormonal changes throughout life, such as during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. These changes can affect thyroid function and increase the risk of disorders.
– Genetic Factors: Thyroid disorders often run in families, and women are more genetically predisposed to conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and management of thyroid disorders in women.
Pregnancy significantly influences thyroid function, making regular monitoring essential for expecting mothers.
– Increased Demand: During pregnancy, the body requires more thyroid hormones to support the development of the baby. This increased demand can sometimes overwhelm the thyroid gland, leading to conditions like gestational hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
– Complications: Untreated thyroid disorders during pregnancy can result in complications such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and developmental issues in the baby.
Regular thyroid screenings during pregnancy help ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
Thyroid disorders can also affect children, though they are often less recognized.
– Hypothyroidism: In children, hypothyroidism can lead to growth delays, intellectual disabilities, and puberty problems. Symptoms might include fatigue, weight gain, and poor school performance.
– Hyperthyroidism: While less common, hyperthyroidism in children can cause symptoms like rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and anxiety.
Recognizing and treating thyroid disorders early in children is vital for their healthy growth and development.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for managing thyroid issues in children.
– Blood Tests: Regular blood tests can help detect abnormal thyroid hormone levels in children. Doctors often use TSH, Free T4, and Free T3 tests to diagnose thyroid conditions.
– Physical Exams: Routine physical exams can reveal signs of thyroid problems, such as changes in heart rate and growth patterns.
Timely screening and diagnosis help manage thyroid issues effectively, ensuring children lead healthy lives.
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of thyroid disorders.
– Family History: Having a family member with a thyroid disorder increases the risk of developing one. Conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease are more common in families.
– Genetic Mutations: Specific genetic mutations can also predispose individuals to thyroid cancer and other thyroid conditions.
Understanding genetic risks can help in early screening and preventative measures for thyroid health.
Genetic testing can provide valuable information about an individual’s risk for thyroid disorders.
– Identifying Mutations: Genetic tests can identify mutations associated with a higher risk of thyroid cancer and other conditions. This information helps personalize screening and treatment plans.
– Family Planning: Genetic testing can guide family planning decisions, helping parents understand the risk of passing thyroid disorders to their children.
Genetic testing is a powerful tool in managing and preventing thyroid health issues.
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports thyroid health.
– Iodine: Iodine is vital for producing thyroid hormones. Foods like fish, dairy products, and iodized salt are good sources of iodine.
– Selenium: Selenium helps in converting thyroid hormones into their active form. Brazil nuts, seafood, and eggs are rich in selenium.
– Zinc: Zinc supports thyroid hormone production and metabolism. Meat, shellfish, and legumes are excellent zinc sources.
Including these nutrients in the diet can help maintain healthy thyroid function.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can interfere with thyroid function and should be consumed in moderation.
– Goitrogens: Foods like cabbage, broccoli, and soy contain goitrogens, which can interfere with thyroid hormone production. Cooking these foods can reduce their goitrogenic effect.
– Excessive Iodine: While iodine is essential, too much iodine can harm the thyroid. It is important to balance iodine intake and follow medical advice.
By avoiding certain foods and focusing on a thyroid-friendly diet, individuals can support their thyroid health.
Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid health by disrupting hormone balance.
– Hormonal Imbalance: Stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that can interfere with the production of thyroid hormones, leading to conditions like hypothyroidism.
– Inflammation: Prolonged stress can cause inflammation, which may worsen autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy thyroid.|
Effective stress management techniques can support thyroid health.
– Exercise: Regular physical activity helps reduce stress and supports overall health. Activities like walking, yoga, and swimming are beneficial.
– Relaxation: Practices like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels and promote mental well-being.
– Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is vital for stress management and thyroid health. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Incorporating stress management techniques into daily routines can positively impact thyroid health.
By considering these factors and implementing proactive measures, individuals can effectively manage their thyroid health. Early detection through regular screenings, genetic awareness, a balanced diet, and stress management are key to maintaining optimal thyroid function and overall well-being.
Maintaining optimal thyroid health requires understanding the complexities of thyroid disorders and the importance of regular screenings. From blood tests and ultrasounds to fine-needle aspiration biopsies and genetic testing, these diagnostic tools play a crucial role in early detection and treatment. It’s essential to consider factors like diet, lifestyle, and stress management, which significantly impact thyroid function.
Regular check-ups and thyroid screenings can catch issues early, preventing serious complications. Women, children, and those with a family history of thyroid disorders should be especially vigilant. By understanding the symptoms and risk factors and by making informed decisions about diet and lifestyle, individuals can profoundly influence their thyroid health.
At Life Imaging Fla, we emphasize the importance of proactive health screenings. Our state-of-the-art imaging technology enables early detection of potential issues, offering peace of mind and a path to timely treatment. Don’t wait for symptoms to disrupt your life—take control of your health today.
Schedule a comprehensive thyroid screening at Life Imaging Fla to ensure your thyroid is functioning optimally. Early detection can make all the difference. Book your appointment now and take the first step towards a healthier future. Visit our website or call us to learn more about our screening services and how we can help you maintain your thyroid health.

Coronary Artery Scan: What It Shows, Who Needs It, and

Fast and Painless Cancer Scan: What It Really Means PREVENTIVE

Fast and Painless Cancer Scan: What It Really Means (and
Introduction Your heart works hard every second of the day,
Introduction Your heart works around the clock, but changes inside

Introduction Your heart works nonstop, often without a single complaint.

* Get your free heart scan by confirming a few minimum requirements.
Our team will verify that you qualify before your scan is booked.
Copyright © 2025 Life Imaging – All Rights Reserved