
Steps to Take for Orlando Residents If Your Heart Scan Shows Abnormal Results
If you live in Orlando and recently had a heart
NOW OPEN! We’re excited to announce our new location in Jupiter, FL is now open! Learn more.

In the medical field, early detection of diseases such as heart disease and cancer is critical. By identifying these conditions in their initial stages, medical professionals can provide timely and effective treatment, significantly improving patient outcomes. Imaging tests are essential tools in this process, enabling healthcare providers to see inside the body and detect abnormalities before symptoms become apparent.
Life Imaging Fla specializes in advanced imaging services designed for the early detection of heart disease and cancer. Utilizing cutting-edge technology and experienced professionals, our imaging center offers a comprehensive range of tests to help identify potential health issues early on. Early detection leads to better treatment options, less invasive procedures, and improved chances of recovery.
Let’s explore the breadth of imaging tests available for early detection. We will delve into various imaging modalities, including CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and more. By understanding how these tests work and their applications, you can make informed decisions about your health. At Life Imaging Fla, our commitment to excellence ensures that you receive the highest quality of care in your journey toward better health. Whether you have a family history of heart disease, cancer concerns, or simply want peace of mind, our range of imaging tests provides the detailed information needed for proactive healthcare management.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scans
CT scans use X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the inside of the body. The patient lies on a table that slides into a doughnut-shaped machine. The machine rotates around the patient, taking many X-ray images from different angles. These images are then combined by a computer to create a cross-sectional view of the body’s internal structures.
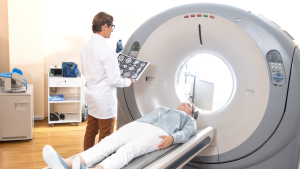
CT scans are commonly used for detecting cancer and heart disease. They can help identify tumors, lesions, and abnormal growths at an early stage. In cardiology, CT scans can detect coronary artery disease, which is a condition where the blood vessels of the heart are narrowed or blocked. This imaging test can also be used to monitor the treatment progress, providing a clear picture of how well interventions are working.
One of the main advantages of CT scans is their ability to provide detailed images quickly. They are also less invasive compared to surgical procedures. This makes them a valuable tool for doctors to diagnose and monitor conditions without exposing patients to much risk. Additionally, the detailed images help doctors plan surgeries better and guide procedures like biopsies.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI scans use strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. Unlike CT scans, MRI does not use X-rays. During the test, the patient lies inside a large tube-like machine. The magnetic fields temporarily realign hydrogen atoms in the body, and radio waves cause these atoms to produce signals. These signals are then used to create images of the inside of the body.
MRI scans are very useful for detecting heart disease and cancer. In cardiology, MRI can evaluate the structure and function of the heart, detect scarring from previous heart attacks, and identify damaged heart muscle. For cancer detection, MRI scans are highly effective in spotting tumors in soft tissues such as the brain, spinal cord, and breasts. MRI is also useful in monitoring how well treatment is working, especially in complex areas like the brain.
The main advantage of MRI is its ability to produce highly detailed images of soft tissues, which X-rays and CT scans may miss. It is particularly good for detecting abnormalities in the brain, muscles, and connective tissues. MRI is also a preferred option when avoiding radiation is important, such as in pediatric imaging or repeated scans.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans
PET scans use a special dye containing radioactive tracers. These tracers are injected into a vein, swallowed, or inhaled. Once inside the body, the tracers are absorbed by the organs and tissues. The PET scanner detects these tracers and creates images that show how the organs and tissues are functioning.
PET scans are particularly useful for detecting cancer and assessing its spread. They can identify malignant tumors and determine if cancer has metastasized to other parts of the body. In cardiology, PET scans can evaluate blood flow to the heart and assess damage after a heart attack. This makes them invaluable for planning treatment and monitoring its effectiveness.
One of the significant advantages of PET scans is their ability to show how organs and tissues are functioning, not just their appearance. This functional imaging provides important information that helps doctors make better treatment decisions. PET scans are often combined with CT scans to produce detailed images that show both the structure and function of the body parts being examined.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to create pictures of the inside of the body. A small device called a transducer sends sound waves into the body, which bounce off tissues and create echoes. These echoes are then turned into images by a computer. Ultrasound is commonly used to examine the abdomen, heart, blood vessels, and other soft tissues.
In cardiology, ultrasound (often called an echocardiogram) can evaluate heart function, measure blood flow, and detect heart defects. For cancer detection, ultrasound can help identify tumors in organs like the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It can also guide needle biopsies, helping doctors collect tissue samples for further examination.
The main advantage of ultrasound imaging is that it is non-invasive and does not use radiation. It is safe for use in pregnant women and children. Ultrasound machines are also generally more accessible and affordable compared to CT or MRI machines, making it easier for patients to get timely diagnoses. Moreover, the real-time imaging capability of ultrasound makes it ideal for guiding procedures such as biopsies and fluid drainages.
Mammography
Mammography uses low-dose X-rays to create images of the breasts. The patient stands in front of a special machine, and the breast is placed on a plate. Another plate then presses down on the breast to spread out the tissue. This compression helps create clearer images and reduces the amount of radiation needed.
Mammography is primarily used for the early detection of breast cancer. It can identify tumors that are too small to be felt by hand. Regular mammograms are recommended for women, especially those over the age of 40, to catch any signs of breast cancer early. Mammography is also used to monitor changes in breast tissue over time, helping doctors identify any areas of concern that may develop.
The main advantage of mammography is its effectiveness in detecting breast cancer early, which significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. The procedure is quick and relatively simple, making it easy to include in routine health check-ups. The use of low-dose radiation also makes it a safe option for repeated screening over time.
Bone Density Scans (DEXA)
Bone density scans, also known as DEXA or DXA scans, use a low dose of X-rays to measure the density of bones. The patient lies on a table while the X-ray machine passes over the body. The scan typically focuses on the hip and spine, which are common sites for fractures.
These scans are primarily used to diagnose osteoporosis, a condition where bones become weak and brittle. Early detection of osteoporosis can help prevent fractures and manage the disease more effectively. Bone density scans are also used to monitor the effectiveness of osteoporosis treatments and measure bone loss in certain medical conditions or after long-term use of medications that affect bone health.
The key advantage of bone density scans is their ability to detect low bone mass well before a fracture occurs. They are quick, non-invasive, and use minimal radiation. These scans provide crucial information that helps doctors develop personalized treatment plans to enhance bone health.
Electrocardiograms (EKG/ECG)
An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart over a period. Small electrode patches are attached to the skin on the chest, arms, and legs. These electrodes pick up the heart’s electrical signals and record them on a graph, showing the timing and duration of each electrical phase in the heartbeat.
EKGs are widely used to detect heart problems. They can identify arrhythmias, heart attacks, pacemaker function, and other heart conditions. In cases of chest pain or shortness of breath, an EKG can quickly help doctors determine if the cause is heart-related. Routine EKGs can also monitor ongoing heart conditions or the effectiveness of treatments.
The primary advantage of EKGs is their ability to provide immediate information about the heart’s electrical activity. The test is quick, non-invasive, and painless. EKGs are excellent for monitoring heart health over time and can help detect issues early, allowing for prompt intervention.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy involves using a flexible tube with a light and camera attached (endoscope) to view the inside of the body. The endoscope is inserted through a natural opening, such as the mouth or anus, or through a small incision. The camera sends images to a monitor, allowing doctors to see the internal structures clearly.
Endoscopy is used to detect problems in various parts of the body, including the digestive tract, respiratory system, and joints. In gastroenterology, it can identify ulcers, tumors, and other abnormalities in the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Bronchoscopy (a type of endoscopy) checks for lung issues. Arthroscopy examines joint problems.
The main advantage of endoscopy is its ability to provide real-time, detailed images of the body’s internal structures. It is minimally invasive, often performed on an outpatient basis, and allows for biopsies and treatments to be done during the same procedure. Endoscopy can help diagnose issues quickly and accurately, preventing the need for more invasive surgeries.
Nuclear Medicine Scans
Nuclear medicine scans involve the use of small amounts of radioactive material to diagnose and treat diseases. The radioactive material is usually injected into a vein, but can also be swallowed or inhaled. Special cameras detect the radiation emitted and create images of the body’s internal structures and functions.
These scans are used for early detection of cancer, heart disease, and bone disorders. For example, a bone scan can identify abnormalities such as fractures, infections, or cancer spread. A myocardial perfusion scan assesses blood flow to the heart muscle and can detect areas with poor blood supply, indicating coronary artery disease.
The significant advantage of nuclear medicine scans is their ability to provide both structural and functional information. They can detect abnormalities at an early stage and help evaluate how well organs and tissues are working. Despite involving radioactive material, they are generally safe, with radiation exposure comparable to that of a standard X-ray.
Fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopy uses continuous X-ray beams to create real-time images of the body. During the procedure, the patient is positioned between an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen. The resulting images are displayed on a monitor, allowing doctors to observe movement and guide procedures.
Fluoroscopy is often used to guide diagnostic and treatment procedures. In cardiology, it helps place stents or perform angiograms. It is also used in gastrointestinal studies to visualize the digestive tract’s function. Fluoroscopy assists in orthopedic surgeries, such as joint replacements, and in guiding catheter insertions in various medical fields.
The real-time imaging capability of fluoroscopy is its main advantage. This allows physicians to observe bodily functions and movements directly, making it invaluable for guiding interventions and ensuring accurate placement of devices. It reduces the need for exploratory surgeries and can improve the safety and effectiveness of various procedures.
Digital X-Rays
Digital X-rays use electronic sensors to capture images of the inside of the body. The sensors convert the X-ray beams into digital images, which can be immediately viewed on a computer monitor. This modern method replaces traditional film-based X-rays.
Digital X-rays are commonly used to diagnose fractures, infections, and tumors. They also monitor treatment progress in lung diseases and check for blockages in blood vessels. In dental care, digital X-rays identify cavities, monitor teeth development, and assess bone health.
Digital X-rays offer several advantages over traditional X-rays. The images are produced quickly, allowing for immediate review and diagnosis. They provide higher quality images, which can be easily enhanced and shared with other healthcare providers. Digital X-rays also use less radiation, making the procedure safer for patients.
Thermography
Thermography uses infrared cameras to measure temperature variations on the surface of the skin. The camera captures the heat emitted by the body and produces color-coded images that show different temperature zones.
Thermography is used for early detection of breast cancer, where it can identify abnormal heat patterns that may indicate the growth of tumors. It is also used to diagnose conditions like inflammation, infections, and blood flow problems. Athletes use thermography to detect injuries and monitor recovery.
The main advantage of thermography is its ability to detect temperature changes that may signify underlying issues before other symptoms appear. It is a non-invasive, radiation-free procedure, making it safe for repeated use. Thermography provides a unique perspective on the body’s function and helps in early diagnosis and preventive care.
Virtual Colonoscopy
A virtual colonoscopy, also known as CT colonography, uses CT scans and computer software to create 3D images of the colon. Before the test, the patient follows a special diet and may take a laxative to empty the colon. During the procedure, a small tube inflates the colon with air or carbon dioxide to get clear images. The CT scanner takes detailed cross-sectional images, which are then processed to form a virtual view of the colon.

Virtual colonoscopy is primarily used to detect colorectal cancer and polyps. It is an alternative to traditional colonoscopy for people who cannot undergo the standard procedure. This test can also identify other abnormalities in the abdomen and pelvis, such as diverticulosis or inflammatory bowel disease.
The main advantage of virtual colonoscopy is its less invasive nature compared to traditional colonoscopy. There is no need for sedation, and the procedure is quicker. It provides clear images that can help detect early signs of colorectal cancer. Recovery time is minimal, and patients can return to their normal activities almost immediately.
Doppler Ultrasound
Doppler ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to measure blood flow through arteries and veins. A hand-held device called a transducer is pressed against the skin over the blood vessels. The device emits sound waves that bounce off moving blood cells, and these echoes are analyzed to produce images and measure blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound is used to diagnose various circulatory conditions, such as blood clots, blocked arteries, and poor blood flow. It is essential for detecting deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and for evaluating the effectiveness of treatments like blood thinners. This test is also used to monitor blood flow in organs and extremities after surgeries.
The significant advantage of Doppler ultrasound is its ability to provide real-time information about blood flow without using radiation. It is non-invasive and generally painless. This method helps doctors diagnose and monitor the treatment of vascular conditions early, potentially preventing serious complications like strokes.
Elastography
Elastography is a specialized form of ultrasound that measures the stiffness or elasticity of tissues. It uses sound waves to create images that show variations in tissue stiffness. The transducer sends out sound waves, which are reflected back and analyzed by a computer to produce a map of tissue stiffness.
Elastography is mainly used to assess liver health. It can detect fibrosis or scarring of the liver, which are key indicators of chronic liver disease. This test is also valuable for evaluating breast lumps and distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors. It helps in the assessment of conditions like chronic hepatitis and fatty liver disease.
The primary advantage of elastography is its ability to provide non-invasive assessment of tissue stiffness, which can indicate disease. This test reduces the need for liver biopsies, making it less invasive and more comfortable for patients. Elastography provides quick results, facilitating the early detection and treatment of liver conditions.
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) uses light waves to take cross-sectional images of tissues, especially the retina in the eye. The patient rests their chin on a support, and the OCT device scans the eye using low-powered light waves. This creates highly detailed images of the retina’s layers.
OCT is most commonly used in ophthalmology to diagnose eye conditions such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. It can also be used to assess and monitor the efficacy of treatments for these conditions. Additionally, OCT has applications in cardiology to visualize the coronary arteries.
The main advantage of OCT is its ability to provide high-resolution images of the retina, helping in the early detection of eye diseases. The procedure is non-invasive, quick, and painless, making it easy for patients. OCT can detect changes in the eye that are not visible in regular eye exams, allowing for timely intervention.
SPECT Imaging
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging uses a radioactive substance and a special camera to create 3D pictures of organs and tissues. The patient is injected with a small amount of radioactive substance that emits gamma rays. The SPECT camera rotates around the patient, capturing data from multiple angles, which a computer then combines into 3D images.
SPECT imaging is used for detecting and monitoring heart disease, brain disorders, and bone problems. In cardiology, it evaluates blood flow to the heart muscle, identifying areas with poor blood supply. In neurology, SPECT can diagnose and monitor brain conditions such as epilepsy, strokes, and brain tumors. It is also used in oncology to locate and assess the extent of cancer.
The primary advantage of SPECT imaging is its ability to provide detailed 3D images of the body’s internal structures and functions. It helps in the early detection of diseases and in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments. Although it involves radioactive substances, the exposure is generally low and considered safe.
Capsule Endoscopy
Capsule endoscopy involves swallowing a small, pill-sized camera that takes pictures of the digestive tract as it travels through. The camera captures thousands of images, which are transmitted to a recorder worn by the patient. These images are then downloaded to a computer for analysis.
Capsule endoscopy is primarily used to examine parts of the small intestine that are hard to reach with traditional endoscopy. It helps diagnose conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and gastrointestinal bleeding. This procedure is also used to identify polyps, tumors, and ulcers in the small intestine.
The main advantage of capsule endoscopy is its ability to provide detailed images of the entire small intestine without invasive procedures. It is painless and does not require sedation or recovery time. This test offers a comprehensive view of the small intestine, which is essential for diagnosing and monitoring various gastrointestinal conditions.
Take Control of Your Health with Advanced Imaging
Early detection plays a vital role in managing and preventing serious health conditions. Advanced imaging techniques like CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and others provide detailed, non-invasive insights into the body’s internal structures. These technologies enable early diagnosis, helping doctors treat conditions more effectively and improving patient outcomes.
By choosing Life Imaging Fla, you gain access to state-of-the-art imaging services that prioritize your well-being. Our skilled team uses the latest imaging technologies to help detect health issues early, allowing for timely and effective treatment. Whether you’re monitoring an existing condition or looking for routine screenings, our comprehensive range of imaging services will meet your needs.
Prioritize your health today by booking an appointment with Life Imaging Fla. Our cutting-edge imaging solutions provide peace of mind and a proactive approach to your health. Early detection can make all the difference in treatment success and overall quality of life. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear; take control of your health now.

If you live in Orlando and recently had a heart

Calcified lymph nodes are small, hard lumps that can develop

Low dose CT scanners are advanced tools that play a

Virtual colonography is an advanced way to check the health

Feeling anxious before a medical scan is common. Many people

Lung cancer is a serious disease that starts in the

* Get your free heart scan by confirming a few minimum requirements.
Our team will verify that you qualify before your scan is booked.
Copyright © 2025 Life Imaging – All Rights Reserved